Parkinson’s disease is one of the most well-known neurodegenerative disorders among the 600+ disorders afflicting the nervous system. This page details the known associated proteins that contribute to the disease.
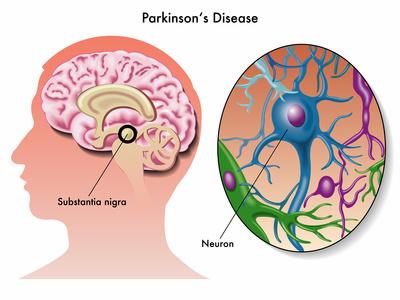
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder after Alzheimer’s disease (AD), affecting 1–2% of the population over age 60. PD is characterized by the progressive degeneration and loss of dopaminergic (DA) neurons in the substantia nigra of the midbrain, and defined in part by the presence of intracytoplasmic inclusions called Lewy bodies (LBs). PD manifests as a variety motor symptoms such as resting tremors, rigidity and postural instability. PD is often accompanied by non-motor symptoms (NMS), which may occur in the pre-motor phase of the disease and include olfactory dysfunction, REM sleep disorder, anxiety and depression. Cognitive impairment affecting executive functions such as attention, recognition, working memory, and problem solving may also appear in the pre-motor phase and progressively increase in intensity leading to dementia in the late phase of the disease.
Sporadic forms of PD constitute the majority of affected population and patients are generally afflicted later in life, with the onset of disease occurring over the age of 60. Individuals with genetically-linked familial forms of PD, represent less than 10% of the patients, and have earlier onset of disease; occurring before the age of 40 or 50. Mutations in the genes that code for α-synuclein, Parkin, leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2), PTEN-induced putative kinase 1 (PINK1), and protein deglycase DJ-1 have been associated with developing PD. Currently, there are no laboratory tests to help diagnose sporadic Parkinson’s disease. A definite diagnosis is only accomplished based on post-mortem immunohistochemical analysis and detection of specific inclusions (LBs) in the brain of affected individuals.
More detailed information can be found at this link: www.biolegend.com
